Routing with Water
PgOSM Flex makes it easy to get started with routing with OpenStreetMap data and pgRouting. The best experience is with pgRouting 4.0 and newer. If you are using a pgRouting prior to 4.0 see Routing Roads: Legacy (pgRouting 3).
Prepare routing edge networks
You should have ran the steps in Prepare for Routing before continuing.
PgOSM Flex includes functions to prepare routing edge networks for data in
osm.water_line by running the appropriate procedure.
These procedures can take a while to run on larger regions, see the Timing section
below for more details.
CALL osm.routing_prepare_water_network();
Routing with Water
PgOSM Flex also includes a procedure to prepare a routing network using
the osm.water_line table.
CALL osm.routing_prepare_water_network();
Find the vertex_id for start and end nodes, similar to approach above
with roads.
WITH s_point AS (
SELECT v.id AS start_id, v.geom
FROM osm.routing_water_vertex v
INNER JOIN (SELECT
ST_Transform(ST_SetSRID(ST_MakePoint(-77.050625, 38.908953), 4326), 3857)
AS geom
) p ON v.geom <-> p.geom < 200
ORDER BY v.geom <-> p.geom
LIMIT 1
), e_point AS (
SELECT v.id AS end_id, v.geom
FROM osm.routing_water_vertex v
INNER JOIN (SELECT
ST_Transform(ST_SetSRID(ST_MakePoint(-77.055645, 38.888747), 4326), 3857)
AS geom
) p ON v.geom <-> p.geom < 200
ORDER BY v.geom <-> p.geom
LIMIT 1
)
SELECT s_point.start_id, e_point.end_id
, s_point.geom AS geom_start
, e_point.geom AS geom_end
FROM s_point, e_point
;
Route, using the directional approach.
SELECT d.*, n.geom AS node_geom, e.geom AS edge_geom
FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT e.edge_id AS id
, e.vertex_id_source AS source
, e.vertex_id_target AS target
, e.cost_length_forward AS cost
, e.cost_length_reverse AS reverse_cost
, e.geom
FROM osm.routing_water_edge e
',
:start_id, :end_id, directed := True
) d
INNER JOIN osm.routing_water_vertex n ON d.node = n.id
LEFT JOIN osm.routing_water_edge e ON d.edge = e.edge_id
;
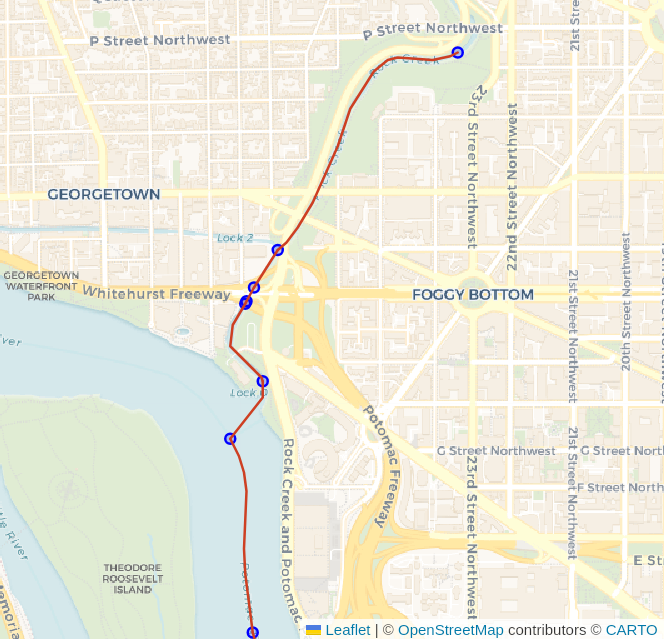
Challenge: Polygons with Water Routing
Waterway routing using lines only is often complicated by the nature of waterways and the way routes flow through steams and rivers (lines) and also through ponds and lakes (polygons). The data prepared by the above procedure only provides the line-based functionality.
The following image (source) visualizes the impact polygons can have on a line-only routing network for water routes.
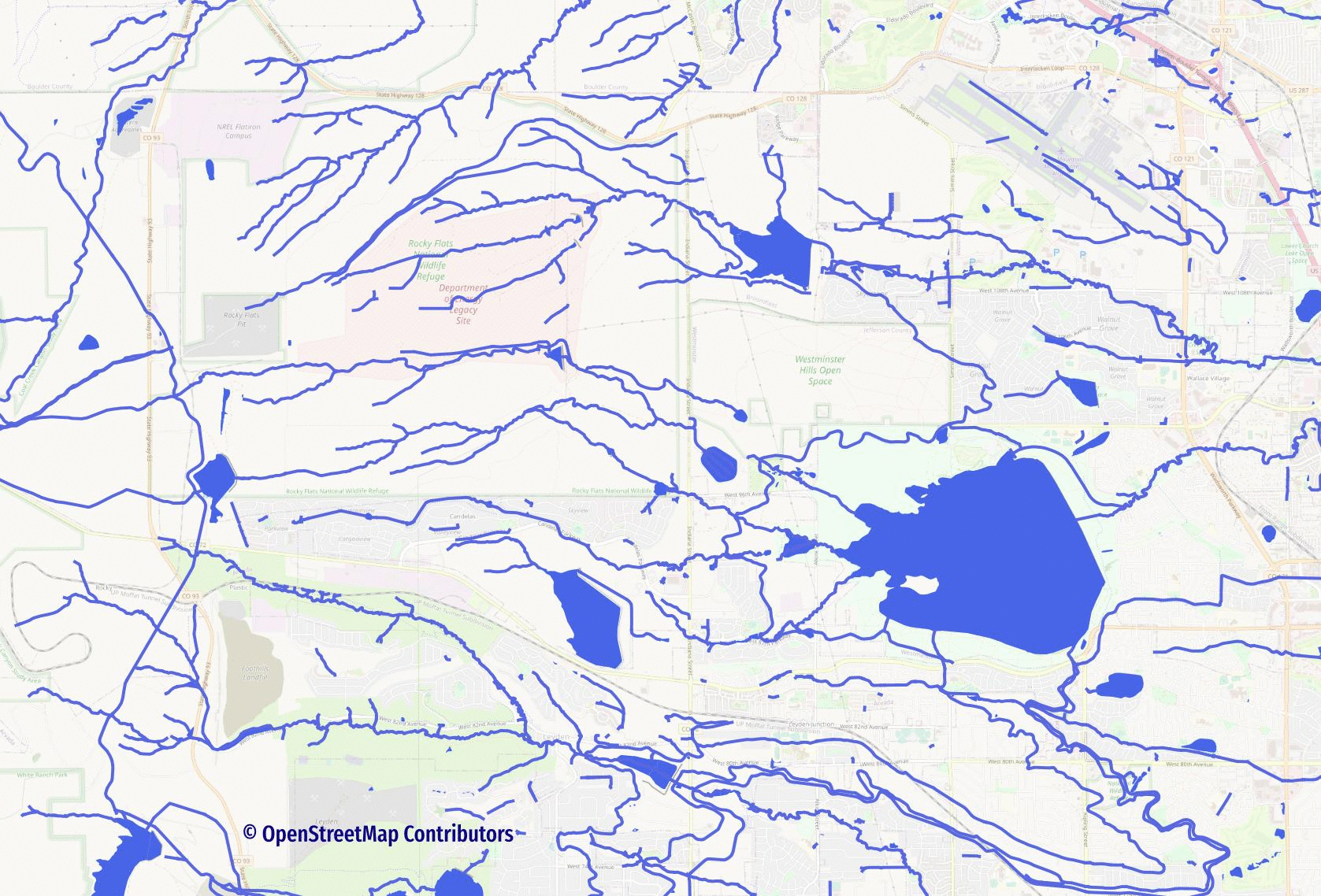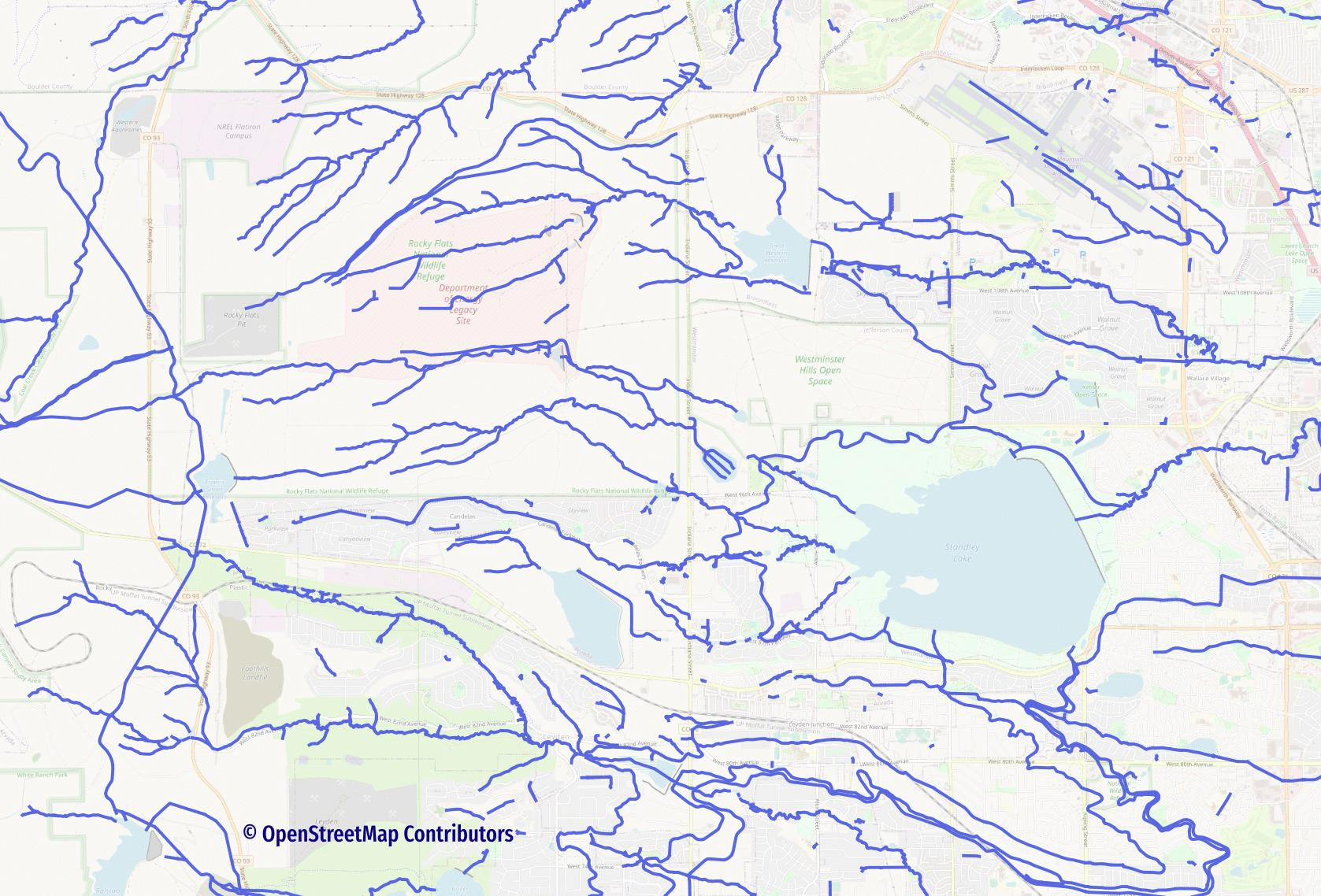
See the Routing with Lines through Polygons blog post to explore one possible approach to solving this problem.