PgOSM Flex on Windows
PgOSM Flex can be used on Windows via Docker Desktop. This page outlines a few Windows-specific steps where they deviate from the experience on Linux.
Install Docker Desktop
The Docker documentation has instructions to install Docker Desktop on Windows. There is a link toward the top of that page to download the latest installer. The installation steps are under the Install Docker Desktop on Windows section, with both interactive and command line instructions.
Note: If your Windows user is NOT the admin, you must also follow the steps to add your user to the
docker-usersuser group. Those steps are listed after the main installation steps.
Create Folder
Create a pgosm-data folder under your user's Documents folder. This gives PgOSM Flex
a place to save files that you can access directly from your host Windows machine.
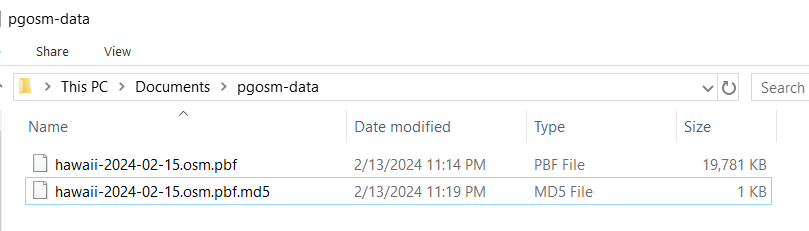
The following screenshot shows this folder with the .pbf and .md5 files downloaded
to load Hawaii from 2024-02-15.
Download PgOSM Flex Image
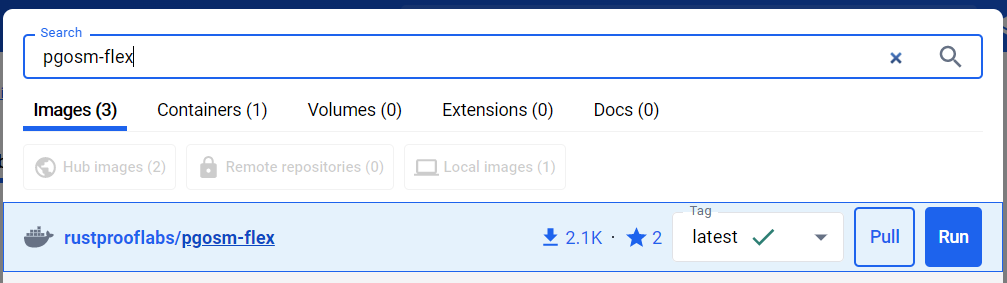
Search for the rustprooflabs/pgosm-flex Docker image via Docker Desktop.
Leave the "Latest" tag selected and click "Pull" to download the image.
Run Docker Container
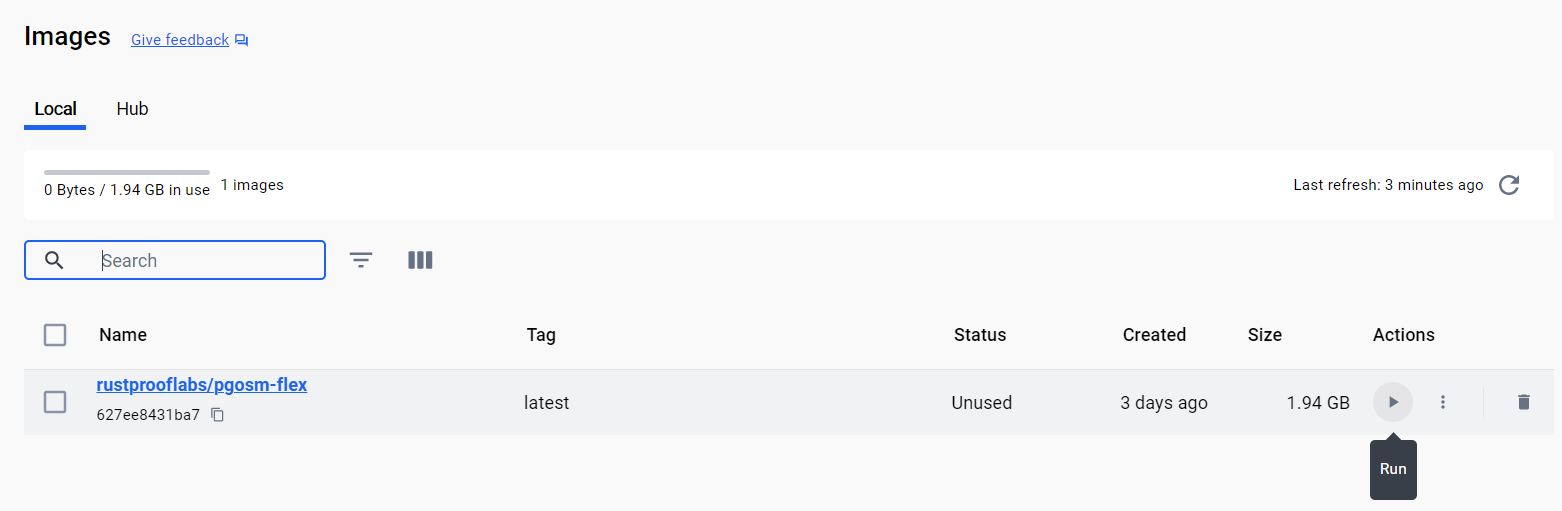
The Images section of Docker Desktop lists the images available on your computer. Click the Run button (play icon) on the right side of the line listing the PgOSM Flex image.
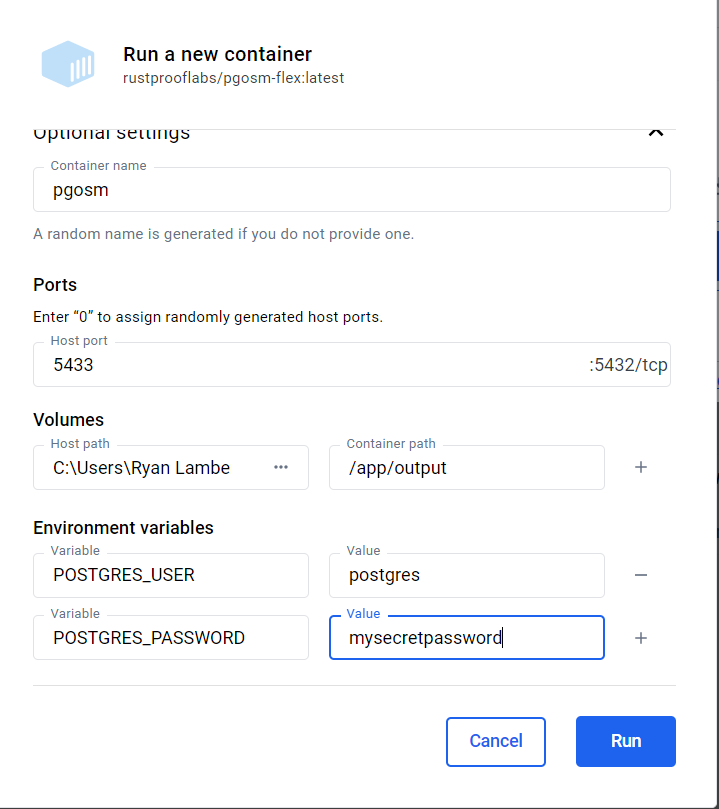
Expand the "Optional Settings" dialog on the Run dialog to enter details to run.
Setting the port to 5433 makes the in-Docker Postgres available to connect to from
your host machine.
The Volumes setting maps your load pgosm-data dirctory (under Documents) to
the Docker container's /app/output directory to make files used available.
The Environment Variables configure the internal database's superuser and password.
DO NOT USE THE PASSWORD SHOWN HERE!
Note: These Windows instructions explain the basic Environment Variables matching the ones used in the main Quick Start guide. There are not equivalent Windows pages for all of the advanced customizations available. For these options, review the main instructions for the command line usage and convert them to the Docker Desktop equivalents.
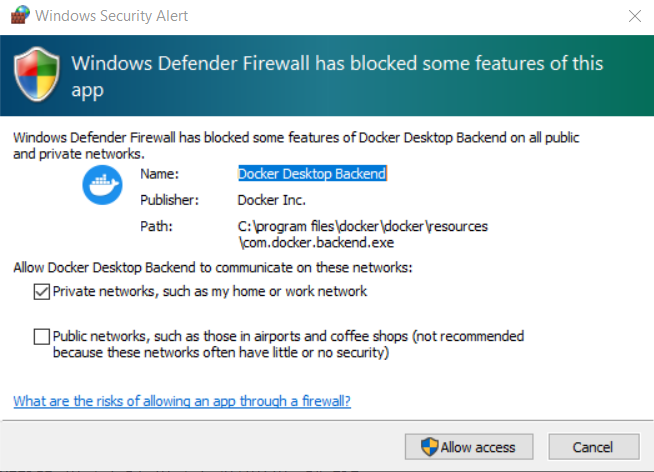
When running the container you might be prompted by Windows Defender about Docker Desktop and the firewall. Most users should click Cancel on this step. You do not need to "Allow access" in order to connect to your Docker container from the computer running Docker.
You should understand the risks of opening up the Postgres port in your firewall. This topic is beyond the scope of this documentation.
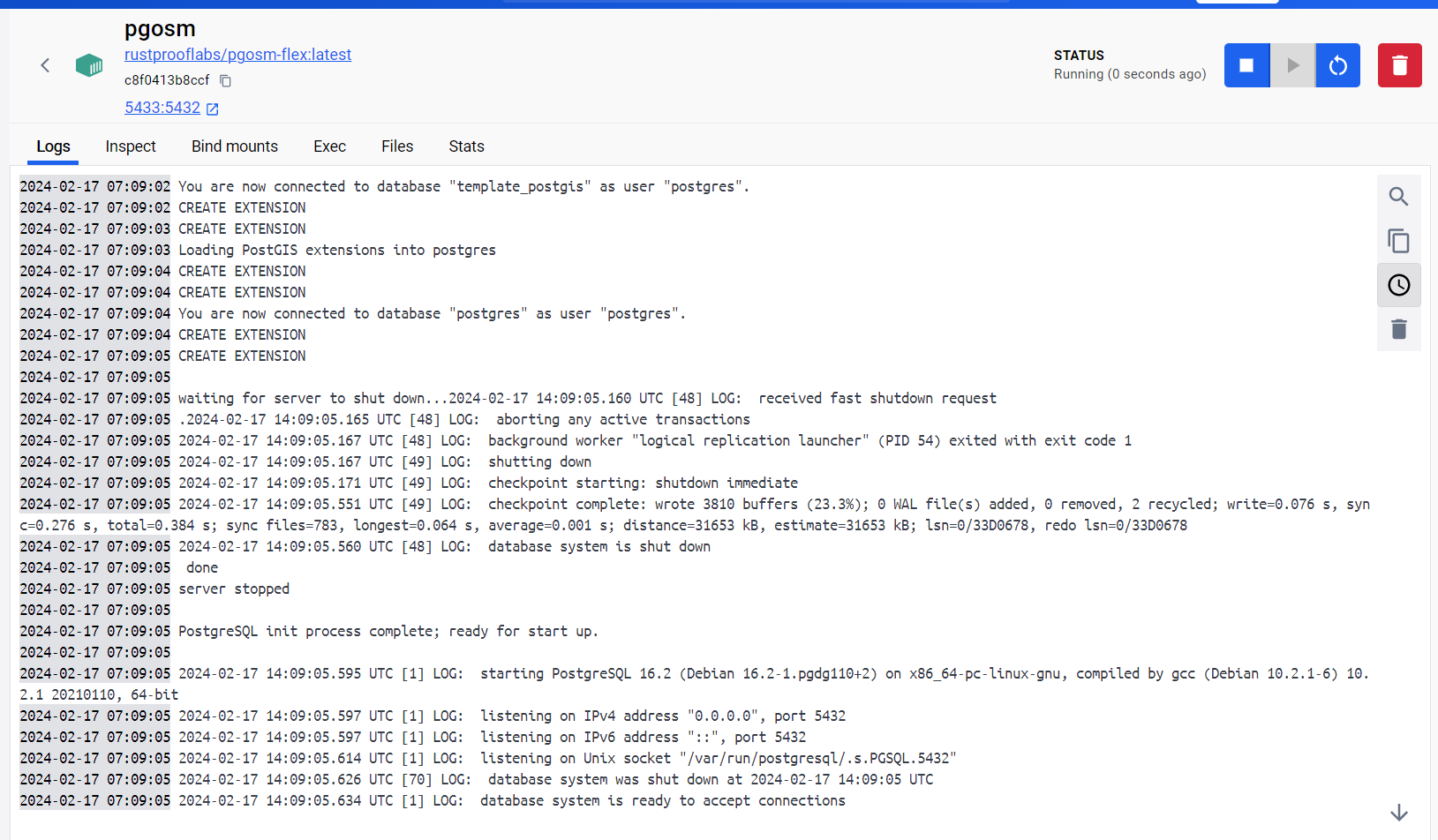
The "Logs" tab for the new running container should display the output from the backend
starting up. The final line from starting up should read
"database system is ready to accept connections." At this point the internal
Postgres service is running and ready.
Docker exec
Switch to the "Exec" tab of the running pgosm container. This interface allows
running commands inside the Docker container. This provides the docker exec -it pgosm
functionality used on the command line elsewhere throughout this documentation.
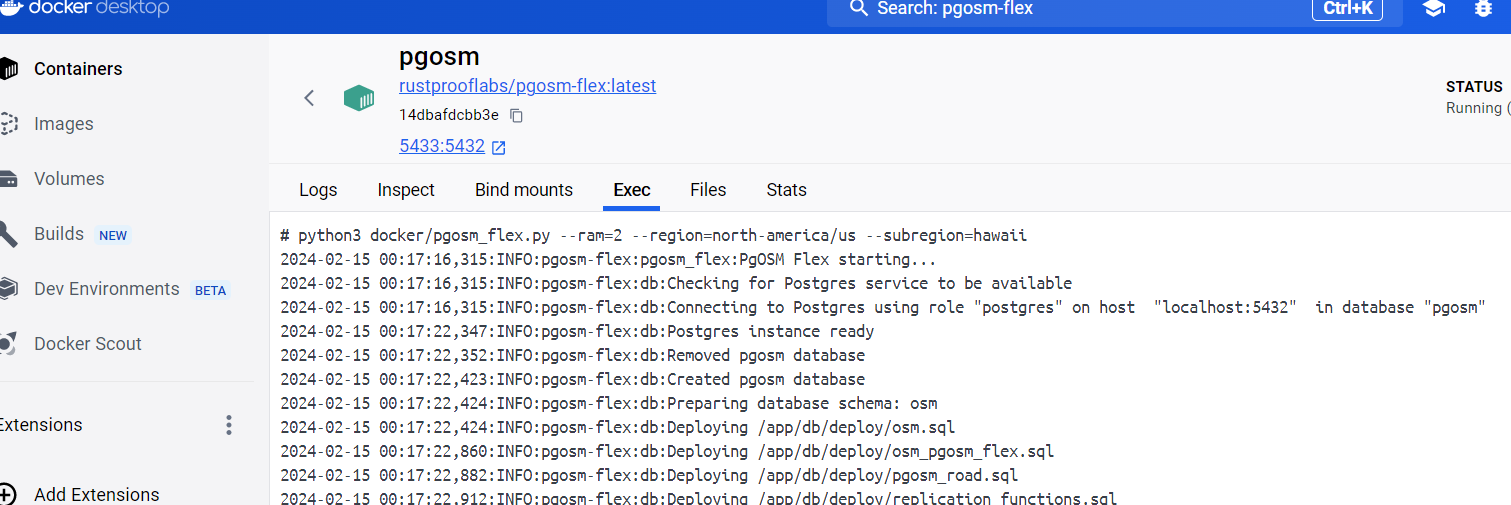
Enter the command to run in the container.
python3 docker/pgosm_flex.py --ram=2 --region=north-america/us --subregion=hawaii
The following screenshot shows this command being ran and the initial portion of the output from processing.
Docker Desktop handles the
execfunctionality. Commands ran via Docker Desktop exclude thedocker exec -it pgosmseen throughout the remainder of this documentation.